Zeppelin Notebook - big data analysis in Scala or Python in a notebook, and connection to a Spark cluster on EC2
Which notebooks for my computations ?
iPython was the first shell to introduce this great feature called “notebook”, that enables a nice display of your computations in a web server instead of a standard shell :
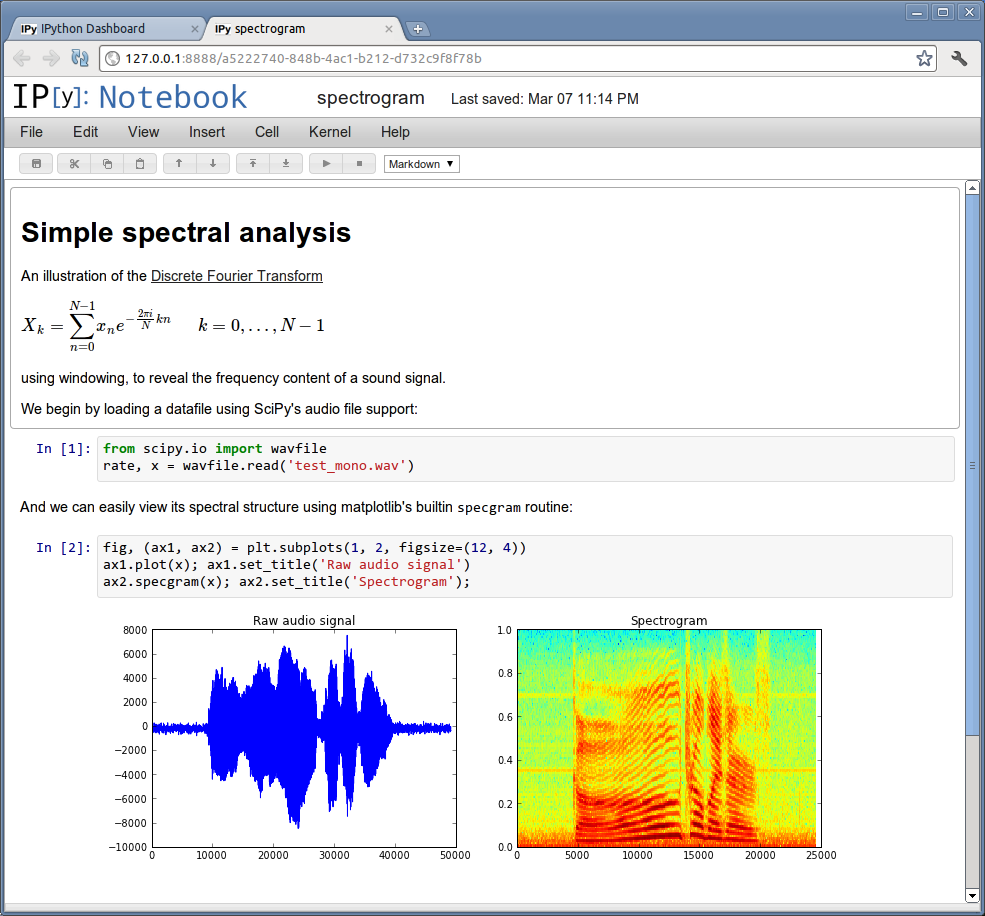
This allows you to share your computations with others, that can understand, modify and adapt to their needs in live.
Originally designed for python programming, the iPython 2 followed with a modular architecture for language plugins, named “kernels”, such as IScala for Scala, or ISpark for Spark.
iPython 3 was competely re-architected and introduced Jupyter, an independant web server. Plugins had to be redesigned as well for compatibility (such as Jupyter-Scala for Scala).
Some specific notebooks appeared for other languages, such as Spark Notebook.
But the most promising one is Zeppelin from Apache Foundation. Zeppelin presents many advantages :
-
simplicity : for beginner or the marketer in the company, it’s easier for him to manipulate the data. In particular thanks to queries in SparkSQL and a nice display widget
-
language-agnostic, with a real plugin architecture, named “interpreters”. The “cluster” function of iPython or SparkNotebook is quite difficult to understand and customize. Scala and Python are the first 2 main languages available.
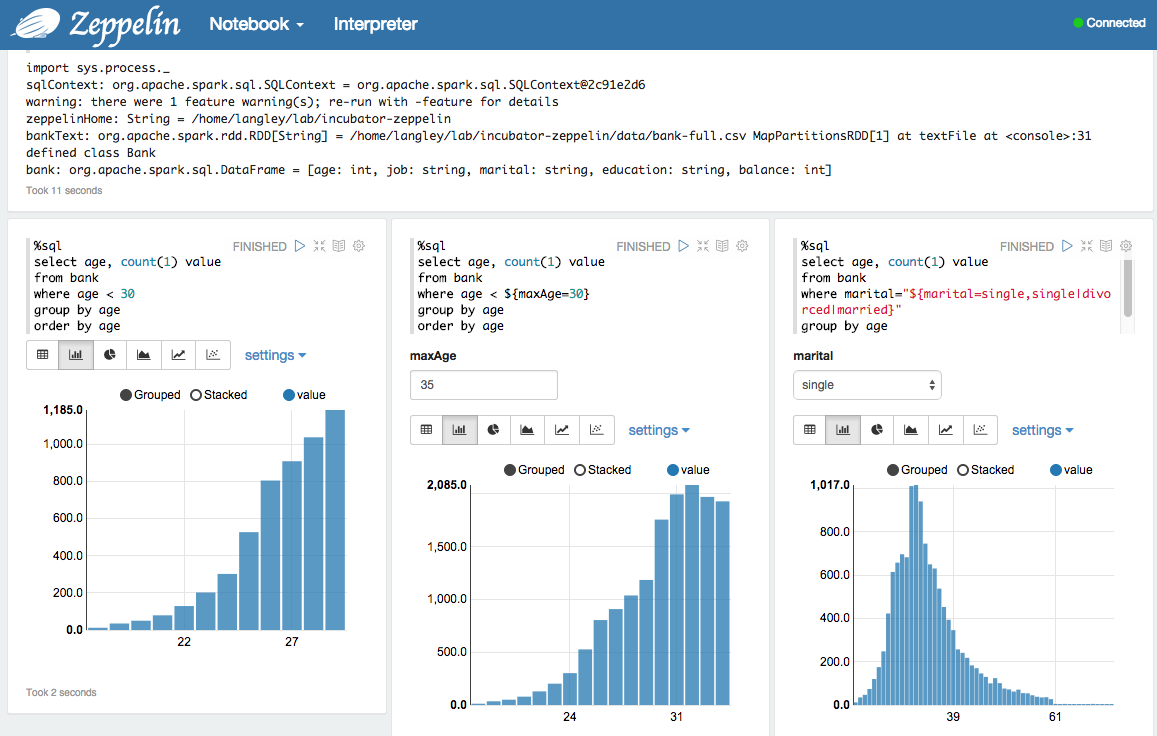
Let’s launch a Spark cluster on EC2 and do some computations in our Zeppelin notebook
Launch of the Spark Cluster on EC2
You need a AWS account, with an EC2 key pair, and credentials with AmazonEC2FullAccess policy.
#download last Spark version for Hadoop 2
wget http://wwwftp.ciril.fr/pub/apache/spark/spark-1.6.0/spark-1.6.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
tar xvzf spark-1.6.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
rm spark-1.4.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
#export the AWS credentials
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=...
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=...
#verify the permissions of the keypair
chmod 600 sparkclusterkey.pem
#launch the cluster with --copy-aws-credentials option to enable S3 access.
cd spark-1.6.0-bin-hadoop2.6
./ec2/spark-ec2 -k sparkclusterkey -i sparkclusterkey.pem \
--region=eu-west-1 --copy-aws-credentials --instance-type=m1.large \
-s 4 --hadoop-major-version=2 launch spark-clusterYour master cluster hostname should appear in the logs :
Generating cluster's SSH key on master...
Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-XX-XX-XX-XXX.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com,XX.XX.XX.XXX' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
Be sure to have following ports open in the master’s EC2 security group (the master security group name is the name of the cluster with ‘-master’ appended, in our case spark-cluster-master) :
-
8080: the Spark master web interface is where the jobs (as well as Spark shells which are long term jobs) are displayed. -
7077: the TCP interface to submit jobs,
both to open for access from the instance on which will be installed the Zeppelin notebook.
Zeppelin install
Download and compile Zeppelin:
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-zeppelin
mv incubator-zeppelin zeppelin-0.5.6
cd zeppelin-0.5.6
mvn clean package -Pspark-1.6 -Phadoop-2.6 -DskipTests
mv conf/zeppelin-env.sh.template conf/zeppelin-env.sh
vim conf/zeppelin-env.shAdd the line :
export MASTER=spark://ec2-XX-XX-XX-XXX.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com:7077
Now it’s time to start (or restart) Zeppelin web server
./bin/zeppelin-daemon.sh startZeppelin interface is available at http://localhost:8080/.
Configure your EC2 Spark Cluster in Zeppelin
Go to the interpreter http://localhost:8080/#/interpreter.
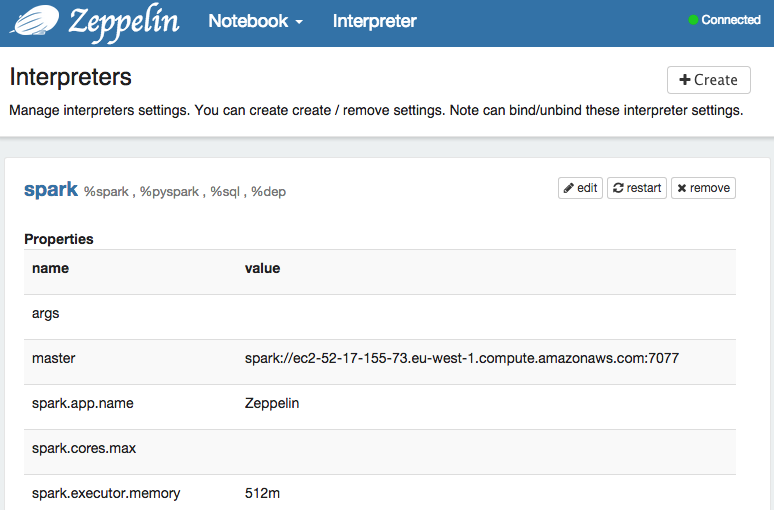
- Edit your ‘spark’ interpreter
- In master property, put (in the place of local[
*]) your master hostname with spark:// at the beginning, and the port at the end, in our example this would bespark://ec2-52-18-32-219.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com:7077. - Save
Now you’re ready for computation
Computations
Create a new Note and open it.
Add a few lines
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("fs.s3n.awsAccessKeyId","YOUR_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID")
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("fs.s3n.awsSecretAccessKey","YOUR_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY")
val file = sc.textFile("s3n://disrupting.fr/samples/")
val reducedList = file.map(l => l.split(" ")).map(l => (l(1), l(2).toInt)).reduceByKey(_+_, 3)
reducedList.cache
val sortedList = reducedList.map(x => (x._2, x._1)).sortByKey(false).take(50)Click on start.
You can see your Zeppelin shell running as an application in the Spark cluster at http://ec2-52-18-32-219.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com:8080/.
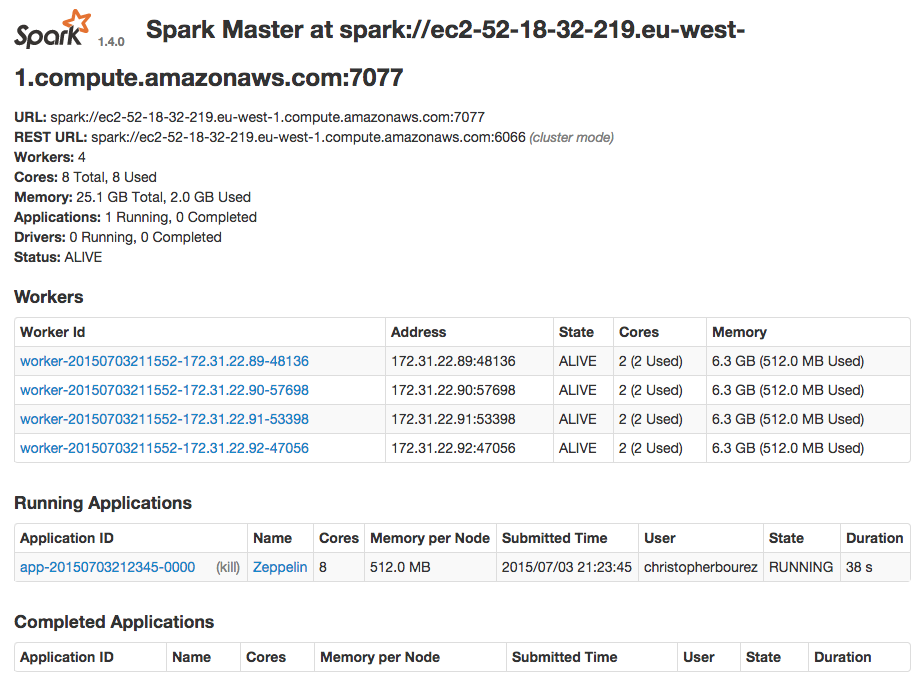
Close
#destroy the cluster
./spark-1.4.0-bin-hadoop2.6/ec2/spark-ec2 -k sparkclusterkey -i sparkclusterkey.pem \
--region=eu-west-1 destroy spark-cluster
#stop zeppelin web server
incubator-zeppelin/bin/zeppelin-daemon.sh stop